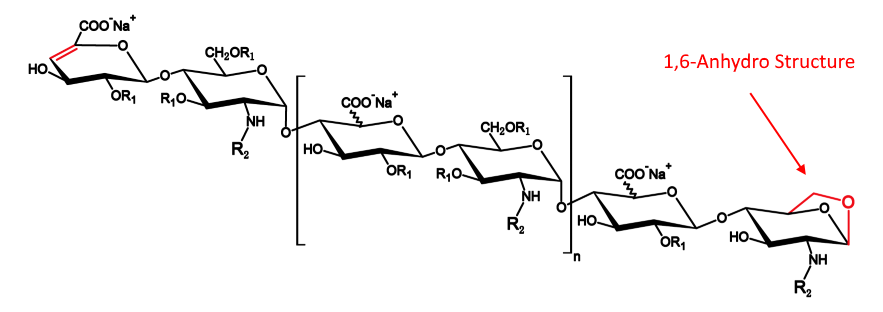
As one of low-molecular-weight heparins (LWMHs), enoxaparin sodium has been manufactured as a generic anticoagulant under different brands, and regulators have been updating requirements. For example, the percentage of polysaccharide chains bearing 1,6-anhydro structure, is a big challenge for enoxaparin manufacturers, according to the test method specified in latest European Pharmacopoeia.
System suitability required by the European Pharmacopoeia Method:
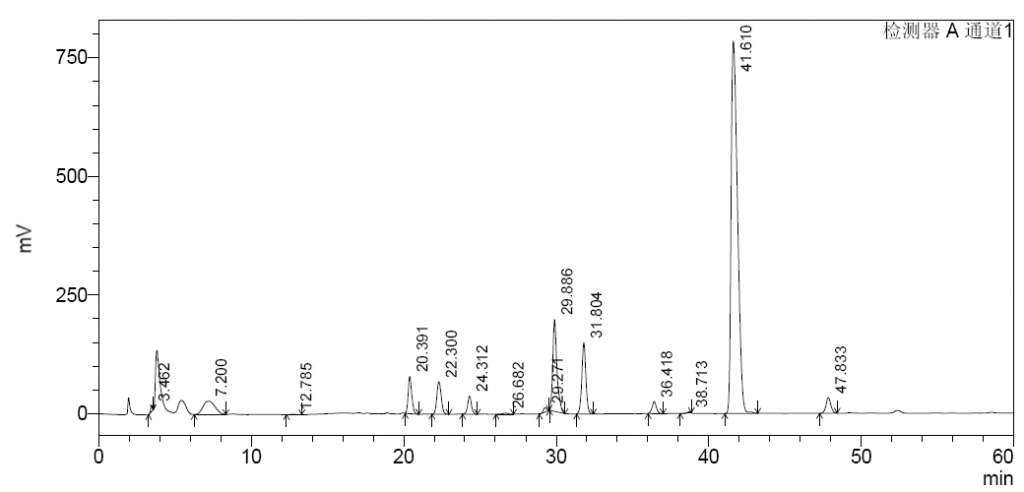
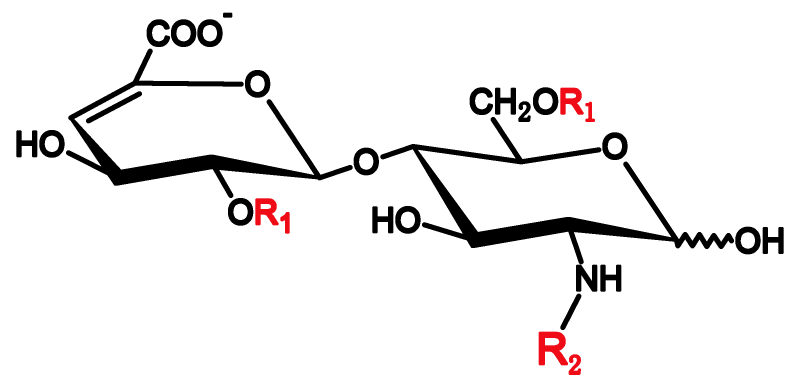
– peak area ratio: maximum 1.15 for the peaks due to 1,6-anhydro ΔIS-IS and 1,6-anhydro ΔIS in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b);
EP9.0 method 1097
– maximum 0.02 for the peaks due to ΔIS and reduced ΔIS in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c);
– resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to reduced ΔIA and 1,6-anhydro ΔIS in the chromatogram obtained with refer-ence solution (c);
– the content of 1,6-anhydro derivatives in enoxaparin sodium CRS is within 1.5 percent of the assigned content.
To test the level of 1,6-anhydro species, a combination of heparinase I, heparinase II and heparinase III is used to degrade enoxaparin samples, followed by reduction via sodium tetrahydroborate. The degraded and reduced sample solutions are injected into a HPLC system for analysis.
To meet the system suitability requirements specified by European Pharmacopoeia, exhaustive depolymerization of enoxaparin samples is necessary. To achieve exhaustive depolymerization, enoxaparin manufacturers tend to use native heparinases with high purity and stability.
Through our experience in serving major enoxaparin manufacturers, Asnail has improved further native heparinases, making 1,6-anhydro derivative test for EP 1079 method more robust and confident. Now we lanuch these heparinases in separate SKUs.
To request a quote, please contact Asnail (info@asnailtech.com).
Besides, we are also developing SAX columns for determining 1,6-anhydro derivatives. Initial tests show good column performance, with the two peaks due to 1,6-anhydro ΔIS and 1,6-anhydro ΔISepi separated clearly. These SAX columns have been used by customers in China.